Definition and Location: Tendonitis, or inflammation of the tendon, refers to the swelling and inflammation of a ligament (tendon). The biceps muscle, located at the front of the arm, has two tendons at the top.
Structure of the Biceps Muscle Tendons
Anatomy: One of these tendons is shorter and attaches to the coracoid process of the shoulder blade, while the other tendon is longer and adheres to the upper edge of the glenoid cavity. This longer tendon passes in front of the head of the humerus and below it, through the bicipital groove located between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus.
Causes of Biceps Tendon Inflammation
Factors Leading to Inflammation:
- Repeated friction of the tendon against surrounding bones within the bicipital groove of the humerus.
- Instability of the tendon within the bicipital groove due to insufficiency of the transverse humeral ligament.
- Rotator cuff tear: Inflammation may occur as a result of a complete or partial tear of the rotator cuff.
Symptoms of Biceps Tendonitis
Main Symptoms:
- The primary symptom of this condition is pain, mostly felt at the front of the shoulder joint.
- The intensity of pain increases when holding objects in front of the body or lifting them overhead.
- Rotating the forearm outward can exacerbate the pain.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Contributing Factors
Causes:
- Impacts of excessive pressures on the tendon.
- Falling on the shoulder, lifting heavy objects, or engaging in intense sports activities.
Diagnosis of the Condition
Diagnostic Methods:
- Ultrasonography is one of the effective methods for diagnosing this condition.
Treatment of Biceps Tendon Inflammation
Initial Treatment Measures:
- Temporarily discontinuing sports activities and avoiding heavy tasks with the hand.
- Refraining from movements that increase shoulder pain.
Auxiliary Methods:
- Using local heat.
- Undergoing physiotherapy.
- Using anti-inflammatory medications.
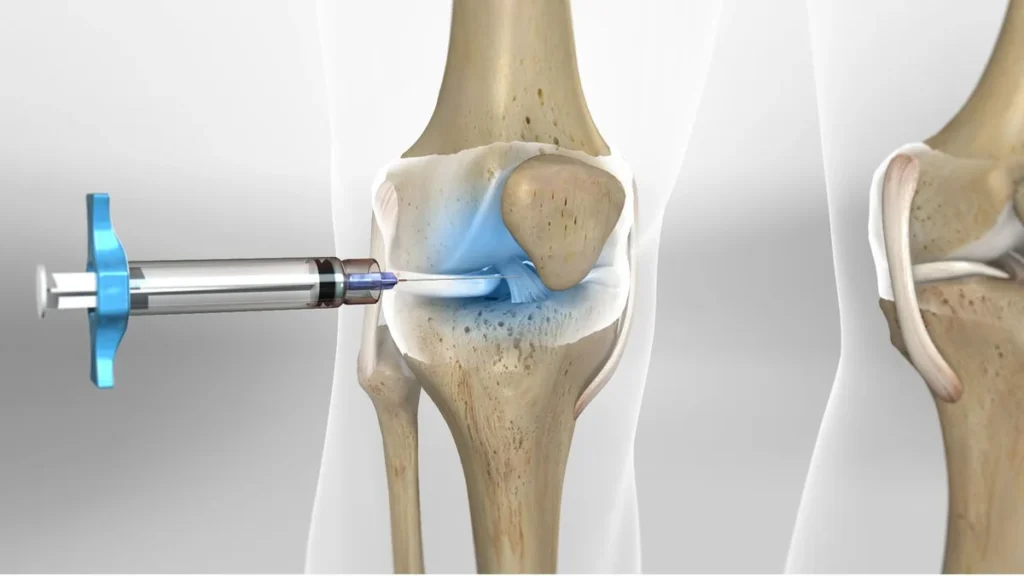
- Medication injection, including corticosteroid injections into the tendon sheath.
Arthroscopic Treatment:
- In cases accompanied by a rotator cuff tear, arthroscopic treatment is performed for rotator cuff repair.
Surgical Measures:
- If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgery is considered.
- The most common surgical methods are tenotomy (cutting the tendon) and tenodesis (attaching the tendon to surrounding tissues).

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.