Introduction: This article, provided by the International Center for Height Increase in Iran, focuses on elbow capitellum fractures.
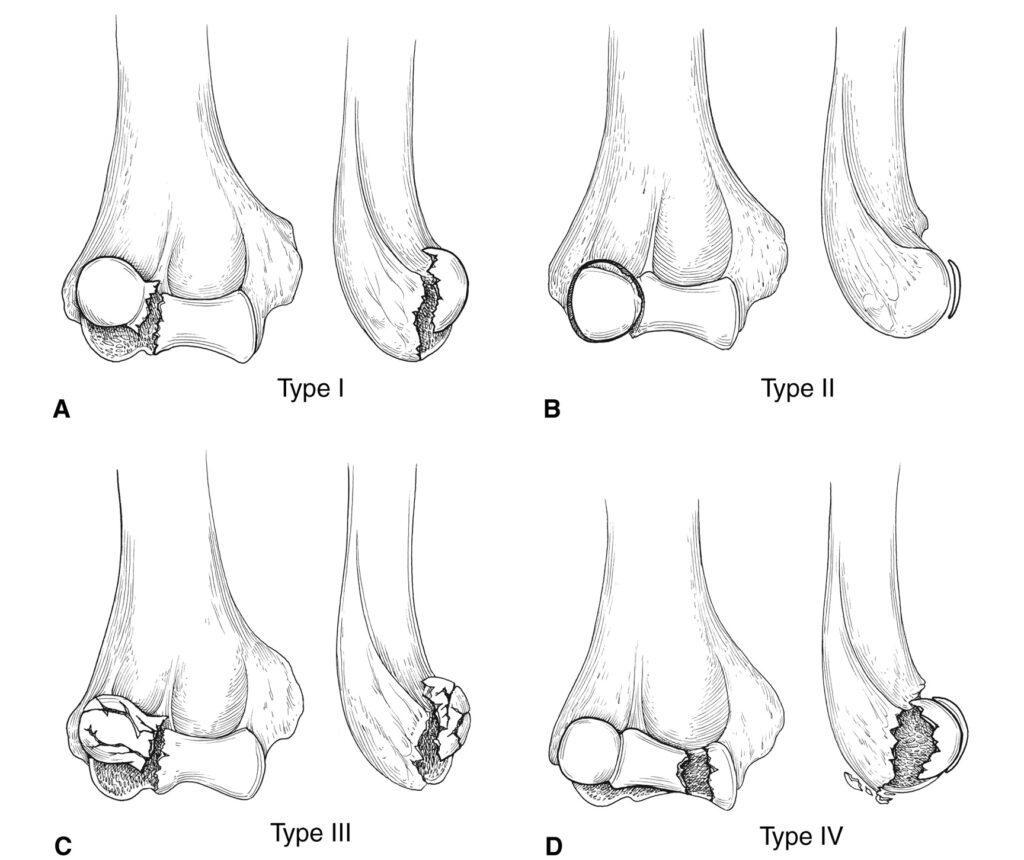
Table Of Contents
- The Structure of the Humerus Bone
- Main Structures of the Humerus Bone in the Elbow Area
- Capitellum: A Key Structure in the Elbow Joint
- Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Symptoms of Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Diagnosis in Radiography
- Treatment of Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Treatment of Non-Displaced Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Treatment of Displaced Elbow Capitellum Fractures
The Structure of the Humerus Bone
The humerus bone is cylindrical. Its upper part forms a spherical head, while the lower part flattens out, forming three distinct structures.
Main Structures of the Humerus Bone in the Elbow Area
- Lateral Condyle (External Lump): An external spherical structure of the bone, known as the lateral condyle.
- Medial Epicondyle: An internal triangular structure, referred to as the medial epicondyle.
- Trochlea: Located between the lateral condyle and medial epicondyle, this structure resembles a pulley and is known as the trochlea.
Capitellum: A Key Structure in the Elbow Joint
- Capitellum Description: Situated in front of the lateral condyle, this hemispherical structure is covered in joint cartilage and articulates with the head of the radius bone. It is known as the capitellum.
Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Cause of Fracture: Most common in adults, these fractures often occur due to falls where the person uses their hand to prevent hitting the ground.
Symptoms of Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Elbow Pain: The primary symptom is pain, particularly on the outer and front side of the elbow. This pain intensifies with pressure on the outer elbow and makes elbow movement painful.
Diagnosis in Radiography
- Simple radiography can reveal the fracture as a piece with a rounded edge in front of the elbow joint.
Treatment of Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Therapeutic Approach: As an intra-articular fracture, it’s crucial to accurately reposition the fractured piece. Otherwise, there’s an increased risk of improper healing and subsequent arthritis in the joint.
Treatment of Non-Displaced Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Using a Splint: If the fracture is completely non-displaced, the main treatment involves immobilizing the elbow using a long arm splint.
- Radiographic Monitoring: The treating physician will monitor the elbow’s condition with weekly radiography during the first three weeks of treatment to ensure no displacement of the fractured piece. After three weeks, the likelihood of displacement decreases, eliminating the need for repeated radiography.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Treatment of Displaced Elbow Capitellum Fractures
- Surgery and Fixation: If the fracture in the capitellum region of the elbow is displaced, it must be repositioned through open surgery and then fixed to the main bone shaft using screws.
- Importance of Accurate Repositioning: Precision in repositioning the fracture is vital. Any misalignment in the joint surface can lead to the development of osteoarthritis in the elbow joint in the future.