In this article, we will discuss the Fracture of the Radial Head in the Elbow.
Initial Explanations and Anatomy Description
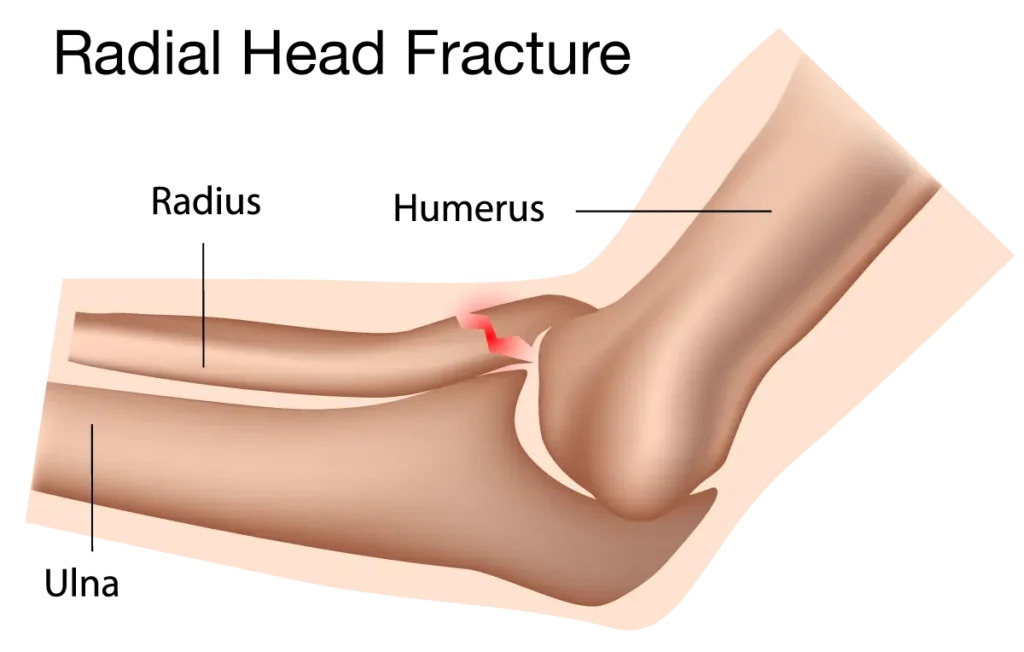
In the elbow area, the lower part of the humerus (upper arm bone) articulates with two bones that form the forearm: the radius (upper or proximal bone) and the ulna (lower or distal bone). The radius has a cylindrical or disc-like structure at its top end, known as the radial head. The upper surface of this disc is concave and articulates with the convex surface of the lateral condyle of the humerus. Just below the radial head is the neck of the radius.
Mechanism of Fracture of the Radial Head in the Elbow Area
Fractures of the radial head are common in young people. They typically occur when a person extends their hand to protect themselves during a fall. The impact of the palm hitting the ground transmits a large force through the forearm upwards, forcefully driving the radial head against the external condyle of the humerus, leading to the fracture.
Types of Fracture
Sometimes, the fracture is minimal, presenting as a vertical crack in the radial head. In other cases, a piece of the radial head may be chipped off like a slice of cake and displaced. Occasionally, the radial head is completely shattered and breaks into several pieces. In severe fractures, the cartilage of the radial head and the capitellum also suffer significant damage.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Radial Head Fracture
Patients with radial head fractures often complain of pain in the outer part of the elbow joint. This pain typically intensifies during rotational movements of the elbow. Pressing on the radial head with a finger can also increase the pain. Generally, severe swelling in the elbow area is not observed, but there may be limited rotation of the forearm.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Treatment of Radial Head Fracture
Diagnostic Methods
For an accurate diagnosis of a radial head fracture, simple radiography is used. Sometimes, it’s necessary to perform radiographs from specific angles of the elbow joint to clearly visualize the fracture line.
Non-surgical Treatments
In cases where the fracture is non-displaced, treatment usually involves the use of a long upper limb splint or suspending the arm from the neck for 2 to 3 weeks. After this period, the patient helps improve elbow movement through specialized exercises.
Surgical Treatments
If the fracture consists of one or two large pieces that can be fixed, the treatment involves surgical intervention to reposition and fix the broken pieces with screws and plates. In cases where there are many broken pieces, the treatment includes surgery to remove the entire radial head.
Fractures in Children
n children, fractures in the discussed area usually occur as fractures of the neck of the radius. In these cases, the fracture line passes below the radial head. If the angulation of the radial head is up to 10 degrees, the treatment involves using a long splint to immobilize the elbow for three weeks. If the deviation is greater, the treatment consists of a closed reduction of the fracture and immobilization using a splint.
By applying this approach to rewriting the text, a clearer and more comprehensible structure is given to the text, and information is presented in a precise and organized manner, aligning with search quality evaluator guidelines.
Potential Complications of Radial Head Fracture in the Elbow
Elbow Joint Stiffness
A significant complication of radial head fracture is elbow joint stiffness. This condition can lead to limited joint mobility. During rehabilitation, it is crucial to perform exercises actively, meaning that the patient should move the elbow using their muscle strength.
Limited Mobility
Excessive pressure applied by a physiotherapist to the injured joint for flexing and extending it can increase mobility limitations in the elbow. Special attention is required during the treatment period to prevent further limitations.
Arthritis or Elbow Joint Wear
If the broken pieces do not heal properly, it can lead to joint surface irregularity, which may eventually cause arthritis or wear of the elbow joint. In the early stages, the problem might be solved by removing the radial head, but in advanced stages, even complete removal of the radial head may not resolve all the patient’s issues.
By applying this structure and approach in rewriting the text, a clear and comprehensible structure is created for the reader, and information is presented accurately and orderly, in line with search quality evaluator guidelines.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.