Introduction to Snapping Scapula Syndrome
Snapping Scapula Syndrome, also known as Snapping Scapula Syndrome, is a condition characterized by a grating or snapping sound in the shoulder during movement. This sound or sensation, akin to objects rubbing against each other, is felt at the back of the chest. These noises and sensations are due to changes in the soft tissue between the shoulder blade and the rib cage, which can become thickened, inflamed, and irritated.
- Introduction to Snapping Scapula Syndrome
- Anatomy of the Shoulder
- Shoulder Movement and Its Role
- Definition and Function of Muscles Around the Scapula
- Bursae and Their Role
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the Bursa
- Causes of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
- Symptoms of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
- Diagnosis of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
- Therapeutic Approaches for Snapping Scapula Syndrome
Anatomy of the Shoulder
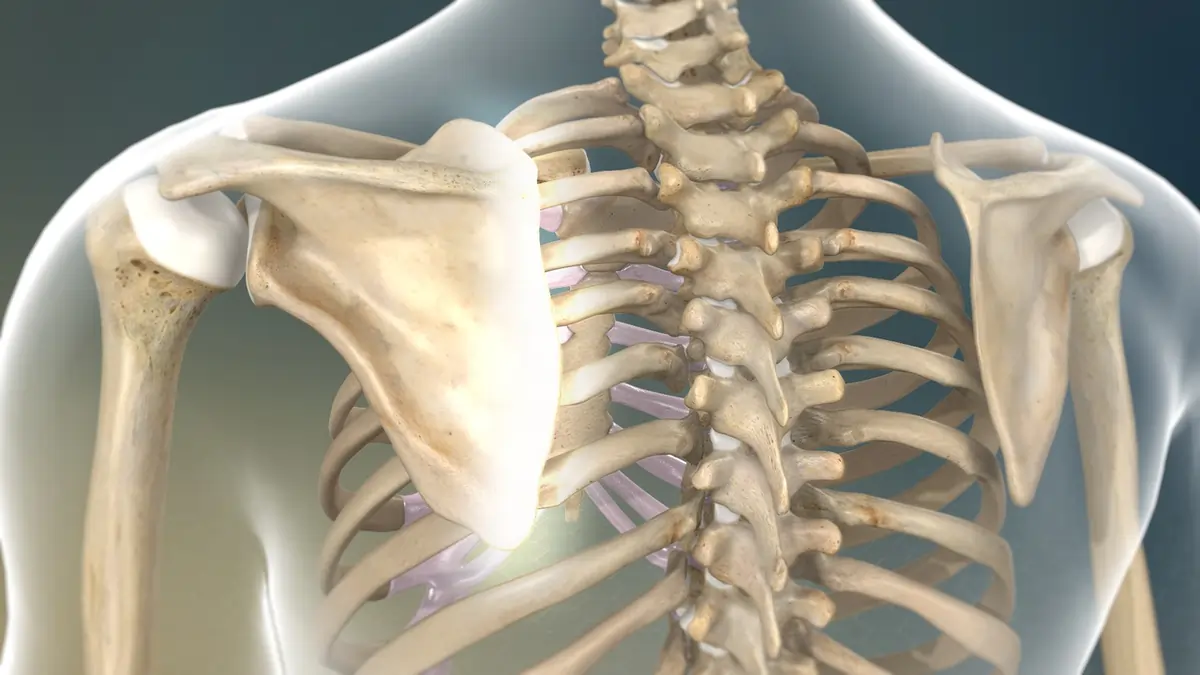
The shoulder blade, or scapula, is a triangular bone located at the back of the chest on both sides of the body. It articulates with the arm bone on one side and connects to the collarbone at the front of the chest.
Shoulder Movement and Its Role
The scapula has a complex movement that aids in arm mobility. When lifting the arm overhead, two-thirds of the movement and rotation occurs in the glenohumeral joint (the joint between the scapula and the arm), and the remaining one-third is due to the rotation of the scapula at the back of the chest. This interaction between the scapula and the chest forms a joint known as the Scapulothoracic joint.
Definition and Function of Muscles Around the Scapula
The anterior or front surface of the scapula is covered by two muscles: the Subscapularis and the Serratus Anterior muscle.
- Subscapularis Muscle: This muscle attaches to the anterior surface of the scapula and connects to the head of the arm bone.
- Serratus Anterior Muscle: This muscle attaches to the inner edge of the scapula and connects to the ribs of the chest.
Bursae and Their Role
A large, flat bursa is located between these two muscles. A bursa is a tissue sac filled with viscous fluid, allowing the two muscles to glide smoothly over each other. Additionally, another bursa is situated between the Serratus Anterior muscle and the ribs.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the Bursa
Sometimes, these bursae become inflamed, a condition known as Bursitis. Inflammation of the bursa in this area, termed Scapulothoracic Bursitis, causes pain and the sensation of sound at the back of the shoulder.
Causes of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
Snapping Scapula Syndrome can arise from several factors:
- Inflammation Due to Repetitive Movements: One of the primary causes of this syndrome is the inflammation of the soft tissue between the scapula and the posterior chest wall due to repetitive movements in certain jobs, like wallpapering, or sports, like baseball pitching.
- Muscular Weakness and Altered Distance Between Scapula and Ribs: Sometimes, weakness or immobility of the muscles between the scapula and the chest causes the scapula to move closer to the ribs. This can create friction over the rib prominences during shoulder movement.
- Bone Deformities: In other cases, deformities in bones, such as poorly healed fractures of the scapula or ribs, can cause abnormal friction.
Symptoms of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
The primary symptom of this condition includes feeling or hearing a grating, snapping, or rubbing sound in the back of the shoulder during shoulder movement. Sometimes, Scapulothoracic Bursitis can also cause pain in the back of the shoulder during movement.
Diagnosis of Snapping Scapula Syndrome
Diagnosis of this condition is usually based on the patient’s description and a physical examination by a doctor. Changes in the shape of the shoulder or chest bones can be observed through simple radiography or CT scans. MRI is a suitable option for examining Scapulothoracic Bursitis.
Therapeutic Approaches for Snapping Scapula Syndrome
Treatment varies depending on the severity and symptoms of the condition.
- Non-Surgical Treatments: In most cases, non-surgical measures are sufficient. These include reducing physical activities that put pressure on the shoulder, performing stretching exercises under a physiotherapist’s guidance, and using cold or warm compresses and anti-inflammatory drugs if pain is present.
- Surgical Methods: If there is no improvement with non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary. Two types of surgery that may be performed for this condition include:
- Spine of Scapula Removal Surgery: This involves removing bony protrusions of the scapula that may rub against the ribs during movement.
- Arthroscopic Bursectomy: In this surgery, the inflamed bursa is removed through arthroscopy.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Thank you for reading about Snapping Scapula Syndrome. Please share your questions and comments with us.