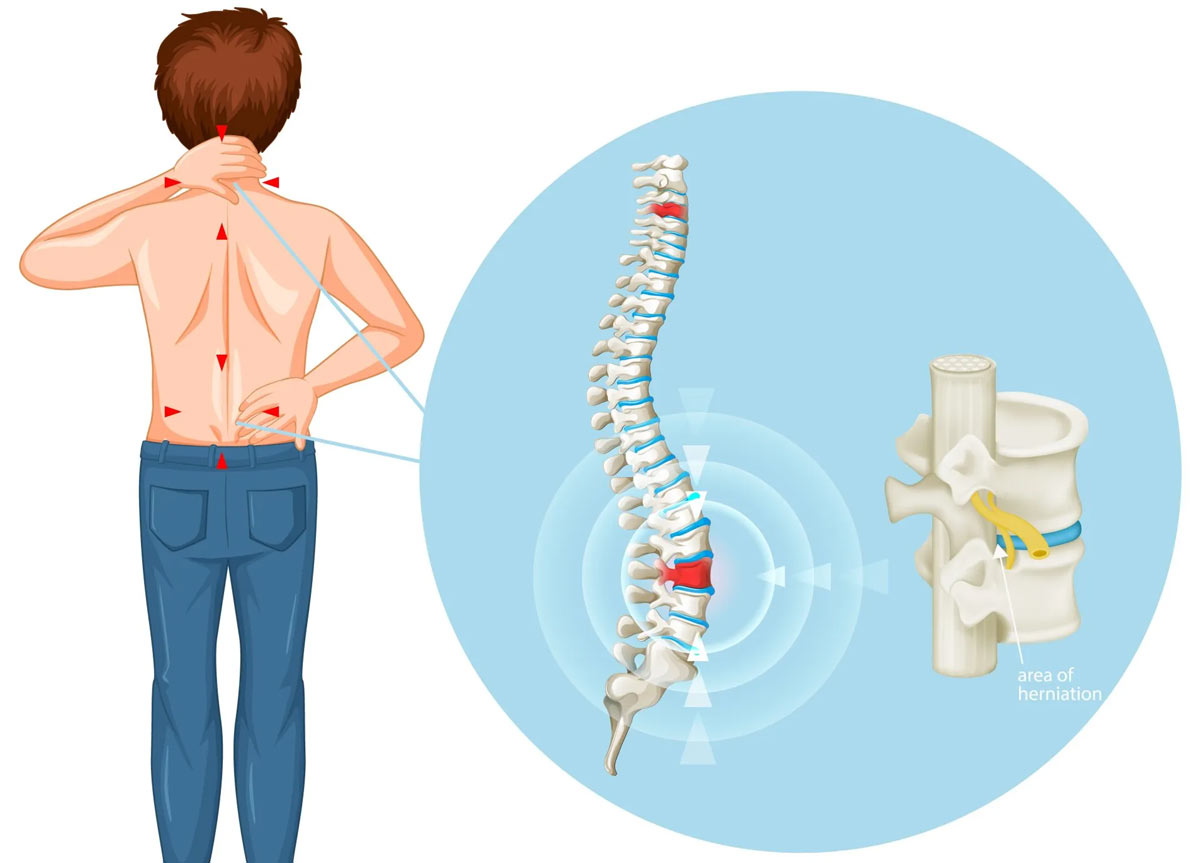
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc, is a condition affecting the discs located between the vertebrae in the spinal column. This issue often begins without any noticeable symptoms but gradually leads to severe pain that can limit a person’s ability to perform daily routine tasks.
- What is a Herniated Disc?
- Where is the Herniated Disc Located?
- The Importance of Treating a Herniated Disc
- Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
- Location of Pain Due to Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Causes of Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Characteristics of Pain Caused by Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Consequences of Lumbar Disc Herniation
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Diagnosis Process for Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Tests for Lumbar Disc Herniation with Descriptions:
- Lumbar Disc Herniation Tests Table
- Treatment Methods for Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Prevention Methods for Lumbar Disc Pain
- Effective Exercises for the Back
- Non-Medical Solutions for Managing Lumbar Disc Pain
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
You may have experienced unexplained back pain at times. This pain could be due to heavy lifting, damage to the vertebrae, or specific diseases. Many people are unsure whether their pain is related to a herniated disc or is caused by muscle spasms in the back. In such cases, specialists in orthopedics or neurology usually diagnose the condition as a disc herniation.
For more information about the location of herniated discs and their associated symptoms, please join us in this article from the Iran Height Increase Center.
What is a Herniated Disc?
The lumbar discs are structures located between the vertebrae of the lower back. They have a jelly-like consistency and are made up of fibrous materials, protecting the vertebrae from pressure. If a disc shifts from its original position, it can exert significant pressure on nearby nerves, causing pain, shortness of breath, and muscle weakness.
A herniated disc has a gelatinous inner part and a tough, elastic outer ring. When doctors diagnose a person with a disc herniation, it means the gelatinous part of the disc has protruded through the outer ring. This condition is also known as disc prolapse.
Where is the Herniated Disc Located?
The spine is composed of several vertebrae stacked on top of each other. In total, there are 33 vertebrae, among which are five lumbar discs connected to the sacrum and coccyx at the end. These discs act like soft, spongy cushions and play an essential role in maintaining the health and proper functioning of the spine. They act as shock absorbers and prevent potential damage to the spine during daily activities.
The Importance of Treating a Herniated Disc
If a herniated disc is not treated, it can lead to severe muscle weakness in the legs and even paralysis. For treatment, it is recommended to consult a subspecialist orthopedic surgeon or contact an orthopedic specialist through online consultation.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
The symptoms of a herniated disc are usually felt on one side of the body, depending on the location and amount of pressure on the nerve. Common symptoms include:
- Tightness in the legs, especially behind the knees
- Tingling or numbness in the area where the nerve is damaged
- Weakness in the muscles around the damaged nerve, which may lead to falls or inability to lift objects
- Leg pain due to disc herniation, which may also be accompanied by pain in the buttocks, thigh, and calf, and may worsen with coughing, sneezing, moving, and standing.
It is better to consult a doctor immediately if you feel any of these symptoms to prevent potential problems through accurate evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Location of Pain Due to Lumbar Disc Herniation
When the inner part of a disc protrudes, chemical substances are released that can irritate nearby nerves, leading to inflammation and pain. Sometimes, due to excessive curvature of the lower back, patients may experience pain in this area. Therefore, back pain is recognized as one of the primary symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation, usually accompanied by stiffness, and patients may also feel pain in their legs.
Causes of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Several factors can lead to lumbar disc herniation, including:
- Obesity: Increases pressure on the spinal discs.
- Trauma: Such as severe falls or impacts that can displace the lumbar disc.
- Accidents: Can lead to disc fractures.
- Improper Movements: Lifting heavy objects or severe twisting during exercise can damage the disc.
- Aging: Over time, discs become dry and weak, and may tear or become brittle.
- Weak Back Muscles: This can increase pressure on the discs.
- Past Surgeries: Can alter the structure of the back and the distribution of body weight, leading to lumbar disc herniation.
Given these factors, paying attention to overall body health, avoiding lifting heavy loads, and taking care of the spine is important for the prevention and treatment of lumbar disc herniation. In case of any pain or symptoms, consulting a doctor is essential.
Characteristics of Pain Caused by Lumbar Disc Herniation
The pain caused by lumbar disc herniation may be mild in some people and not produce many symptoms. However, in many cases, affected individuals feel pain in their lower back and legs. The pain is usually described as a tingling sensation in the legs and is exacerbated by standing, sudden movements, quick turns, and sitting for long periods.
Consequences of Lumbar Disc Herniation
The spinal cord continues as nerve roots below the lower back, known as the “cauda equina.” Sometimes, a lumbar disc herniation can exert excessive pressure on these nerve roots. Without timely diagnosis and treatment, this pressure can lead to severe weakness or even paralysis of the legs.
When to Consult a Doctor
You should immediately consult a subspecialty orthopedic surgeon if you experience the following issues:
- Worsening symptoms
- Negative impact on daily life
- Difficulty in walking or standing
- Bladder and bowel dysfunction
- No improvement of symptoms after 4 to 6 weeks
Diagnosis Process for Lumbar Disc Herniation
A subspecialty orthopedic surgeon conducts a physical examination to diagnose lumbar disc herniation. The surgeon may ask you to lie down on a bed and bring your legs together. In this position, the doctor will be able to assess:
- Your ability to walk
- The strength of your leg and back muscles
- Involuntary body reactions
- Your ability to feel slow strokes, vibrations, and scrapes
Sometimes, for a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor may need to perform additional tests.
Tests for Lumbar Disc Herniation with Descriptions:
- X-Ray: This test is performed to examine the condition of the vertebrae in the spinal column and identify any potential problems.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Uses magnetic images to more accurately diagnose the location of disc herniation and damaged nerves.
- Myelogram: This test is conducted to observe and examine the spinal cord and spinal canal, identifying damaged nerves, spinal tumors, and abscesses.
- CT Scan: A high-precision imaging method used for diagnosing and confirming damaged discs.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures the electrical activity of muscles during contraction and rest to assess muscle function.
- Nerve Conduction Study (NCS): This study measures the ability of nerves to transmit electrical signals between two different points to evaluate nerve function.
Lumbar Disc Herniation Tests Table
These tests assist the doctor in providing a more accurate diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation problems and in devising a more appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Methods for Lumbar Disc Herniation
Home Treatment and Lifestyle Changes
Many people with lumbar disc herniation use home treatments and changes in their daily activities. This includes reducing heavy activities and allowing more time for rest.
Medication Treatment
If lumbar disc herniation has progressed to the point where medical treatment is needed, various medications are used to control pain and inflammation:
- Topical ointments such as Rumathex
- Pain relievers like Diclofenac and Naproxen
- Cortisone medications like Gabapentin and Pregabalin
- Steroid injections into the epidural space of the spine to reduce swelling and inflammation
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapists teach proper movement techniques, lifting, and walking. They help strengthen the muscles of the back and legs with specialized exercises.
Surgical Treatment
In cases where pain and symptoms are due to nerve damage and do not improve with medication, surgery is considered:
- Discectomy: Removing part or all of the damaged disc to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Laminectomy: Removing part of the vertebral lamina to provide more space for the nerves.
- Microendoscopic Discectomy: Removing the disc and fusing the vertebrae together to increase spinal column stability.
These treatment methods help patients continue their daily activities with minimal pain and difficulty.
Complications of Lumbar Disc Surgery
Lumbar disc surgery may have some complications. During the operation, nerves may be damaged or the dura may be torn. Post-surgery, the patient may face problems such as infection, persistent pain, or recurrent lumbar disc herniation.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Prevention Methods for Lumbar Disc Pain
Although it is not always possible to prevent lumbar disc herniation, several measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintaining physical fitness
- Avoiding long periods of driving
- Using shoes with appropriate heels
- Avoiding sitting or standing for long periods
- Sleeping on the side instead of on the stomach
- Regular exercises to strengthen muscles
- Avoiding sudden movements
- Lifting heavy objects by bending the knees, not the back
- Avoiding nicotine use
- Maintaining proper body posture while walking, sleeping, standing, and sitting
Effective Exercises for the Back
Contrary to the belief that continuous rest is necessary, appropriate exercises can help reduce the symptoms of back pain. Below are some recommended exercises and how to perform them:
For a healthy back and to prevent pain caused by lumbar disc herniation, the following exercises can be beneficial:
Hanging Exercise:
- Sets: Three sets, each lasting 30 seconds
- How to Perform: Hang from a bar similar to a pull-up bar with both hands to reduce pressure on the lumbar disc. Stop immediately if you feel pain.
Cat-Cow Movement:
- Sets: Two to three sets, 10 repetitions each
- How to Perform: In a four-legged position, bend your stomach towards the ground and look up at the ceiling. Then, with an exhale, raise your back towards the ceiling and round your spine.
Bird Dog Exercise:
- Sets: Two to three sets, 10 repetitions each
- How to Perform: In a four-legged position, simultaneously lift your left hand and right leg, keeping your torso and knee aligned. Repeat with the other hand and leg.
Plank Exercise:
- Sets: Two to three sets, each lasting between 10 to 30 seconds
- How to Perform: Lie on your stomach and lift your body using your elbows and toes, ensuring your body forms a straight line.
Standing Extension Exercise:
- Sets: Two to three sets, 10 repetitions each
- How to Perform: Stand up and place your hands on either side of your lower back. Push your pelvis forward and bend your spine backward.
Aerobic Exercises:
- How to Perform: Swimming, cycling, and walking are recommended as aerobic activities suitable for the back.
These exercises help strengthen the muscles around the spine and reduce pressure on the lumbar discs. Always exercise caution and avoid sudden, careless movements when performing these exercises.
Non-Medical Solutions for Managing Lumbar Disc Pain
Some non-medical methods that can help relieve lumbar disc pain include:
- Acupuncture: Using thin needles to stimulate specific points on the body to reduce pain.
- Heat Therapy: Using heat to reduce muscle tension and increase blood circulation.
- Cold Therapy: Using cold to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Chiropractic Massage: Specific massage techniques for realigning the spine and reducing pain.
It’s important to note that back pain is not always due to issues with the spinal discs. Therefore, if you experience symptoms of pain in the lower part of the spine, it is advised to immediately consult an orthopedic subspecialist or a neurology subspecialist.
Summary
This article aims to provide comprehensive information about lumbar disc herniation and effective strategies for managing its symptoms. We invite you to share your experiences and opinions on this topic with us, so that others may benefit from your insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Warning Signs of Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Some symptoms may indicate a serious condition of lumbar disc herniation. These symptoms include:
Pain while walking: If back pain is only felt during walking.
Increased pain during sleep: If back pain worsens during sleep.
Numbness on one side of the body: If a part of the body, especially one side, becomes numb.
Weakness in the legs: If you experience weakness in the legs and difficulty in movement.
What are the Risk Factors for Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing lumbar disc herniation:
Obesity: Excess weight can put significant pressure on the spine.
Genetics: Sometimes lumbar disc problems are hereditary.
Physically demanding jobs: Jobs that require lifting heavy weights or repetitive motions.
Smoking: Tobacco use can damage spinal health.
What Medications are Effective for Relieving Lumbar Disc Pain?
For quick relief of pain caused by lumbar disc herniation, the following medications can be used:
Naproxen: A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that helps reduce inflammation and pain.
Ibuprofen: Another anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug effective in reducing disc pain.
Diclofenac: A strong medication used to control severe pain.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.