Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is a common foot condition, primarily causing numbness, burning, tingling sensations, and pain in the sole. This syndrome typically occurs in people who spend a lot of time standing and less time sitting, especially those who work in standing positions for extended periods.
This condition is also known as “TTS” or “Neuropathic Pain in the Ankle” and is treated by doctors using various methods such as rest, steroid injections, or bandaging.
Causes of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome arises when a nerve called the “tibial nerve” at the back of the inner ankle is compressed, leading to various symptoms of pain and discomfort in the foot. It is similar to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, which affects the wrist.
Potential Causes of TTS
The causes of TTS can vary widely. Some factors that may contribute to the development of this syndrome include:
- Having high arches or flat feet.
- Presence of heel spurs.
- Bone protrusions in the tarsal tunnel.
- Inflammation due to rheumatoid arthritis.
- Acute or osteoarthritis.
- Ankle joint arthritis.
- Lesions or masses like tumors near or within the tibial nerve.
- Foot injuries that may lead to ankle sprains or inflammation.
- Varicose veins surround the tibial nerve, increasing pressure on the nerve.
- Diabetes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Occupations requiring prolonged standing, such as sales, security, or hairstyling.
- Wearing inappropriate footwear that can damage the foot.
- Neuropathic diseases and problems.
- Inflammation of the synovial membrane.
- Enlargement of blood vessels.
- Peripheral neuropathy problems.
- Swelling due to pregnancy or other reasons.
- Weight gain.
These factors can independently or collectively contribute to the development of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. If you experience symptoms of this syndrome, it is advisable to consult your doctor for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome are usually observed in the ankle area, sole of the foot, or toes. The following are some of the key symptoms of this condition:
- Pain: Typically felt in the sole of the foot as a burning or shooting pain, which decreases with rest and reduction of activities related to standing.
- Numbness or Burning Sensation: Experienced in the sole of the foot and the first four toes.
- Sensation of Cold or Warmth: In the upper or lower parts of the foot.
- Swelling: Around the lower ankle and the ankle bone.
- Itching: In the ankle area.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
For diagnosing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, doctors use various physical tests focusing on the sole of the foot or the lower foot areas. Questions about the symptoms mentioned above are also asked to provide a more accurate diagnosis. Diagnostic tests and methods include:
- MRI Imaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the ankle.
- Electrical Tests for Nerves and Muscles: Such as nerve and muscle conduction studies (Electromyography).
- X-Ray Imaging: Of the targeted area.
- Muscle Electrophysiology.
Treatment Methods for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
The treatment of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome involves various methods that can help alleviate the symptoms of this condition. Here are some of the main treatment approaches:
- Rest: One of the first and simplest therapeutic measures. Resting the feet reduces swelling and improves symptoms. Lack of rest may increase pressure on the lower foot and exacerbate the syndrome.
- Applying Ice to the Foot: Using ice helps reduce inflammation. Wrap an ice pack in a towel and place it on the ankle area for 20 minutes each time, keeping the lower foot elevated for more effective treatment and pain relief.
- Casting the Foot: In severe cases, the doctor may fully cast the foot to limit movements, gradually aiding nerve, joint, and surrounding tissue recovery.
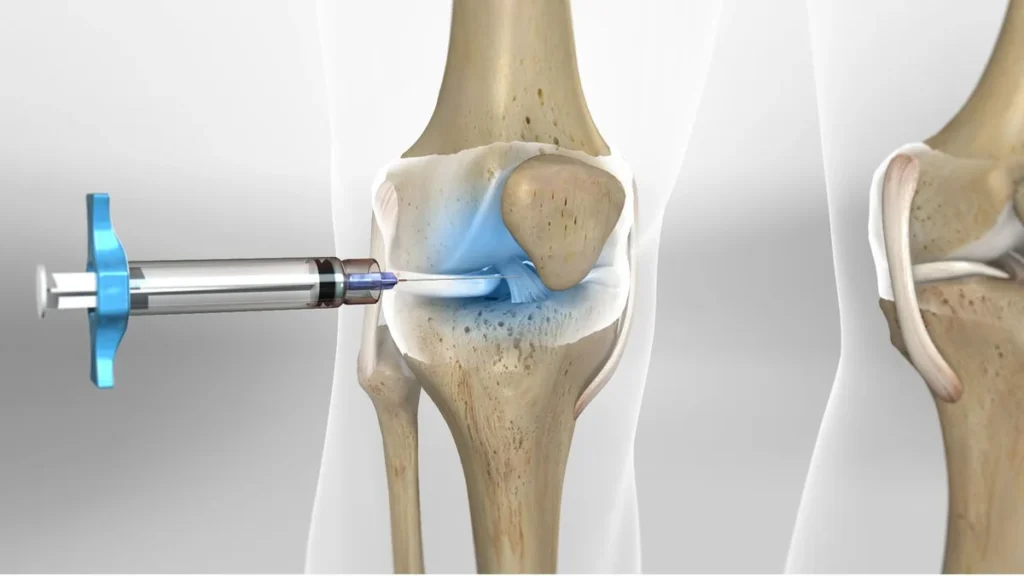
- Injecting Anti-Inflammatory Medications: In cases of severe pain, anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids or local anesthetics may be injected directly into the nerve area, reducing TTS pain.
- Orthopedic Shoes and Devices: Special shoes designed to exert minimal pressure on the nerve and reduce inflammation may be recommended. These shoes often limit foot movement and provide support for the foot arch, effectively treating TTS. Shoes preventing inward twisting or turning of the foot may also be suitable for individuals with TTS.
- Reducing Foot Pressure: If not using orthopedic devices, wearing looser and larger socks and shoes can prevent constriction and worsening of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome pain.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy exercises can help reduce pain and symptoms of TTS. These include strengthening connective tissues, mobilizing the tibial nerve area, and creating space in the joint area. If physiotherapy exercises do not result in improvement, other methods like electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, magnet therapy, etc., are usually employed. Other physiotherapy methods for TTS treatment include:
- Shockwave Therapy: The doctor treats the foot area with sound waves for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Acupuncture: Involves medical history review, and examination of tongue color, shape, and coating. Specific tests are conducted to ensure the suitability of acupuncture.
- Bandaging or Bracing: Prescribed braces by a physiotherapy specialist restrict movements of the foot and ankle, reducing pressure on the tarsal tunnel.
- Exercise Therapy: Involves exercises preventing foot twisting or similar problems, targeting mobility in the ankle, toes, and heel.
- Laser Therapy: Uses lasers to aid in nerve cell recovery and activation of the body’s lymphatic system, blocking pain signals to the brain, thereby treating Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome.
- PRP Therapy: The use of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is another treatment method for TTS, helping in the regeneration of inflamed or deteriorating tissues.
- Ozone Therapy: Another treatment for TTS, ozone therapy activates the body’s antioxidant system, having positive effects on the body.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery
If the pain caused by Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is so severe that it becomes intolerable, or if the conservative treatments previously mentioned are ineffective, surgery might be the only remaining option. This surgery can help reduce pain associated with the syndrome by cutting or reducing pressure in the tarsal tunnel. The procedure involves creating an opening either arthroscopically or by making an incision around the medial malleolus area of the tarsal tunnel.
Surgical Procedure Details
- Duration: The surgery typically takes up to 60 minutes and does not require post-surgical medical care.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia or sedation can be used during the surgery, allowing you to be awake but not feel pain in the surgical area.
During the surgery, the flexor retinaculum is first cut, and then the surgical area is carefully examined. Other parts that may be cut during the surgery include the upper, lower, and middle canals of the tarsal tunnel. If the surgeon observes cysts or damaged tissues in the surgical area, they are also removed, and the fibrous bands causing pressure on the tibial nerve are severed.

To make an appointment or get an online consultation with Dr. Nader Motallebi Zadeh, Limb lengthening surgeon, proceed here.
Final Remarks
In this article, we have comprehensively discussed Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, its causes, symptoms, and treatments, and now you are familiar with this syndrome. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments section.