Amputees with Short Residual Limbs
A short residual limb, also known as an amputation stump, is the remaining bone section after an amputation that is shorter than planned. Generally, surgeons attempt to maintain as much residual stump length as feasible. Nonetheless, the pre-operative diagnosis that led to the amputation typically influences the amputation level and the length of the residual limb.
A particular minimum length of the residual limb is required for the severed limb to function with a prosthesis. There is no standard minimum or optimal length for an amputated bone segment. It depends on the required functionality. A short residual limb restricts both the sort of prosthesis that can be used and the patient’s ability to manipulate it.
For instance, a patient with a very short upper tibia (shinbone) may not be able to get a below-the-knee prosthesis. But, if the short tibial remnant is lengthened, this may become viable. The same holds true for a patient whose forearm stump is short. The residual radius and ulna bones can be extended to allow prosthetic fitting below the elbow.
Patients with short femoral (thigh bone) remnants may be unable to get an above-the-knee prosthesis. In such circumstances, a hip disarticulation prosthesis that is bulkier, heavier, and less functional may be necessary. Bilateral short femur amputees also struggle with sitting balance. The lengthening of bilateral amputees’ residual femur will simplify prosthesis fitting above the knee and improve sitting balance.
Greater demand for lengthening short residual limbs
Greater functional expectations of today’s amputees have increased the demand for lengthening short residual limbs. Prior to twenty years ago, the majority of amputees merely desired to be able to walk again using a prosthetic limb. Many amputees would like to not only walk but also run and participate in sports. Several patients with an amputated limb are investigating whether lengthening their residual limb may enable them to live more active lives in order to fulfill this increased functional demand.
Treatment options
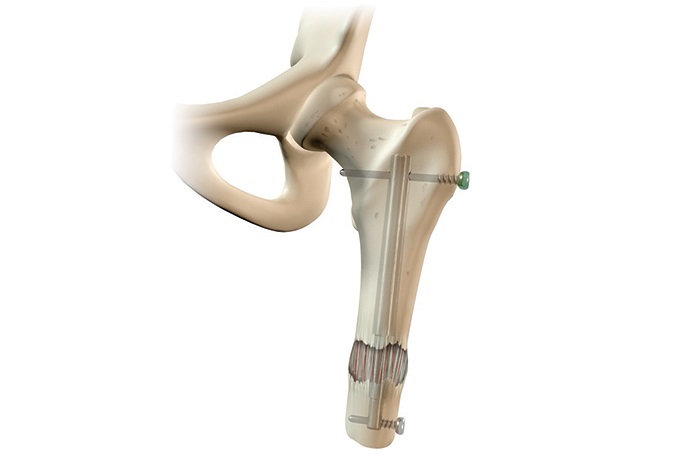
Options for treating amputees with short residual limbs include modifying the stump prosthesis and/or elongating the residual limb. Typically, limb lengthening is accomplished by connecting an external fixator and then performing an osteotomy (bone cut). Adjustments are made daily to the external fixator to gradually extend the bone. With short residual femurs in above-knee amputations, fitting prostheses might be particularly difficult. The Precice Freedom Nail from NuVasive is intended to lengthen short above-knee amputation stumps without requiring an external fixator. The patient may be able to be more physically active if the residual limb is lengthened.